The Discovery of the Ancient Roman Gladiator Games
The ancient Roman gladiator games stand as a remarkable testament to the grandeur and brutality of Roman entertainment. These spectacles, born from humble beginnings, evolved into extravagant displays of combat prowess that enthralled the masses. The discovery of the origins of gladiator games unveils a fascinating journey from solemn funeral rites to the glitzy arenas where warriors clashed in deadly duels. As the games gained popularity, they became intertwined with Roman culture, shaping societal values and norms through the blood-soaked sands of the arena.

Origins of Gladiator Games
Exploring the historical significance and cultural impact of the ancient Roman gladiator games, shedding light on the origins, types of gladiators, arenas, spectators, and the eventual decline of this brutal form of entertainment.
The origins of gladiator games in ancient Rome can be traced back to the Etruscans, who held funeral games to honor deceased warriors. These solemn events gradually transformed into grand spectacles that captivated the Roman populace. The early gladiator contests were intimate affairs, held in makeshift arenas, but as the popularity grew, they evolved into elaborate shows that played a significant role in shaping societal norms.
Gladiator games became a reflection of Roman values, showcasing concepts of honor, courage, and skill in combat. The bloodshed and drama in the arena captivated the audience, providing a form of entertainment that blended violence with spectacle. As the games expanded in scale and complexity, they became a symbol of Roman power and prowess.
The evolution of gladiator games mirrored the shifting dynamics of Roman society, with emperors using these spectacles to gain favor with the people and assert their authority. The games became ingrained in the cultural fabric of Rome, with different classes of society participating in and influencing the spectacle.
Overall, the origins of gladiator games highlight the intersection of tradition, entertainment, and societal values in ancient Rome, laying the foundation for a form of entertainment that would captivate audiences for centuries to come.
Q: Were gladiator games always deadly?
A: While the gladiator games were brutal and often deadly, not all fights ended in death. Some bouts were fought to submission rather than to the death, and certain rules and protocols were in place to ensure the safety of the combatants, at least to some extent.
Q: Did women attend gladiator games?
A: Women were generally not allowed to attend gladiator games in ancient Rome. These events were considered too violent and inappropriate for women to witness, and the audience was predominantly male.
Q: How were gladiators viewed in Roman society?
A: Gladiators occupied a complex position in Roman society. While they were admired for their skill and bravery in the arena, they were also seen as social outcasts and often viewed with a mix of fascination and disdain.
Q: What role did gladiator games play in Roman politics?
A: Gladiator games were often used by emperors and politicians as a way to gain popularity and showcase their power. These events could sway public opinion, serve as a form of propaganda, and even be used to distract the population from political unrest.

Types of Gladiators
When it comes to the ancient Roman gladiator games, the variety of gladiator classes is truly fascinating. These gladiators were not merely fighters but skilled performers who each brought a unique style and weaponry to the arena. Among the most renowned types of gladiators were the murmillo, known for their distinctive helmet and sword, the retiarius who wielded a trident and net, and the secutor who specialized in close combat with a sword and shield.
Each type of gladiator had its own set of armor and combat techniques, creating a diverse and thrilling spectacle for the spectators. The murmillo, with their heavy armor and iconic fish-shaped helmet, symbolized strength and resilience in the arena. In contrast, the nimble retiarius relied on speed and agility to outmaneuver their opponents, using their net to ensnare and their trident to strike. The secutor, on the other hand, epitomized skill and precision, engaging in intense one-on-one combat that showcased their expertise in close-quarters fighting.
These distinct classes of gladiators not only entertained the crowds but also reflected the diverse martial skills and strategies of ancient Rome. The gladiator games were not just about brute force but also about strategy, agility, and showmanship, making each battle a spectacle of skill and courage.
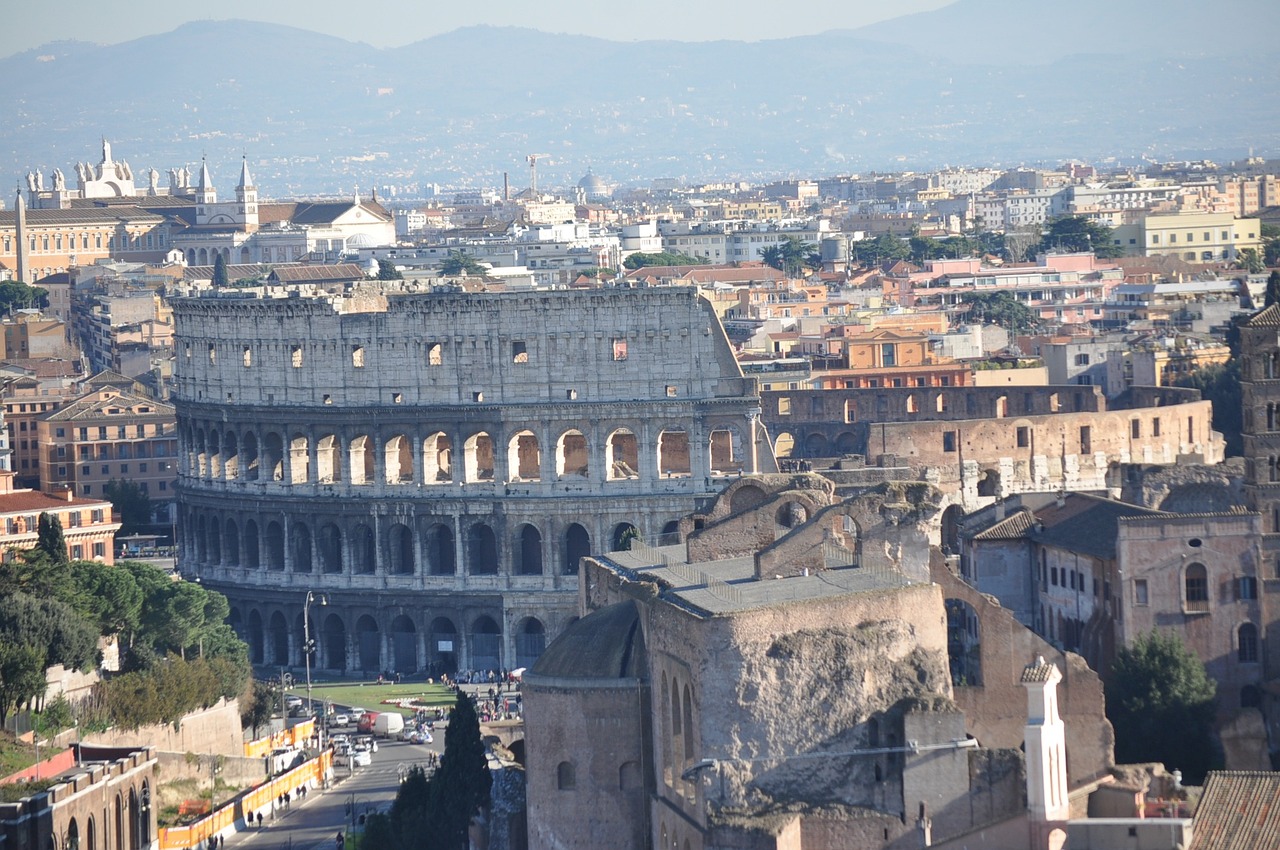

Gladiator Arenas
Exploring the historical significance and cultural impact of the ancient Roman gladiator games, shedding light on the origins, types of gladiators, arenas, spectators, and the eventual decline of this brutal form of entertainment.
Tracing the roots of gladiator games in ancient Rome, examining how they evolved from funeral rites to grand spectacles that captivated the Roman populace and played a role in shaping societal norms.
Detailing the diverse classes of gladiators, such as the murmillo, retiarius, and secutor, each with unique weapons, armor, and fighting styles, showcasing the variety and skill involved in these deadly combat displays.
Unveiling the architectural marvels of Roman amphitheaters like the Colosseum, where gladiator games took place, exploring the design, seating arrangements, and engineering feats that made these venues iconic.
Delving into the social dynamics of Roman audiences at gladiator games, analyzing the fervor, class distinctions, and political undertones that characterized the spectator experience in the ancient world.
Offering insights into the rigorous training regimens and harsh realities of gladiator life, discussing the recruitment, daily routines, and the mix of fame and infamy that awaited these combatants.
Examining the rules and rituals governing gladiator combat, including the strategies, weaponry, and tactics employed in the arena, shedding light on the brutal but structured nature of these fights.
Investigating the factors that led to the decline of gladiator games in Roman society, exploring the moral shifts, economic pressures, and changing tastes that eventually spelled the end of this ancient blood sport.
Reflecting on the enduring legacy of gladiator games in popular culture, art, and literature, considering how these spectacles continue to fascinate and inspire modern audiences, keeping alive the memory of this ancient tradition.
Gladiator arenas were architectural wonders in ancient Rome, with the most famous being the Colosseum. These massive amphitheaters were meticulously designed to accommodate thousands of spectators, with tiered seating providing optimal views of the brutal combat below. The engineering feats of these arenas, such as elaborate underground passages for gladiators and wild animals, showcased the ingenuity of Roman construction.

Spectator Culture
When it comes to the ancient Roman gladiator games, one cannot overlook the vibrant and complex that thrived within the grand amphitheaters of the time. Imagine being a part of the bustling crowd, eagerly anticipating the clash of gladiators in the arena, the air thick with excitement and anticipation. The spectators, ranging from the common citizens to the elite classes, all gathered under the vast dome of the Colosseum, united by their shared love for the brutal spectacle unfolding before them.
Within the amphitheaters, the social dynamics were palpable, with each section of the seating designated for different classes of society. The higher the social status, the closer to the action one would be seated, showcasing the rigid hierarchy prevalent in Roman society. The cheers, jeers, and roars of the crowd reverberated through the stone walls, creating an electrifying atmosphere that fueled the combatants in the arena.
Moreover, the gladiator games were not merely entertainment but also held political undertones. Emperors and politicians often used these spectacles as a means to gain favor with the populace, showcasing their power and generosity by hosting lavish games with exotic animals, elaborate sets, and grand displays of wealth. The cheers of the crowd could sway the decisions of those in power, making the spectator experience a potent tool in the political landscape of ancient Rome.

Gladiator Training and Life
Gladiator training and life in ancient Rome were harsh and demanding, shaping individuals into skilled fighters through rigorous preparation and discipline. To become a gladiator, individuals often came from varied backgrounds, including prisoners of war, slaves, and volunteers seeking fame and fortune in the arena. Upon entering a ludus, a gladiator training school, they underwent intense physical conditioning and combat training under the watchful eye of experienced instructors known as lanistas.
The daily routines of gladiators were strict and focused, consisting of grueling exercises, weapon drills, and simulated combat to hone their skills and build endurance. They adhered to a spartan lifestyle, with limited food and basic accommodations, fostering camaraderie and a sense of brotherhood among fellow trainees. The path to becoming a successful gladiator was paved with challenges and sacrifices, as they faced the constant risk of injury or death in the arena.
Gladiators were categorized into different types based on their fighting styles and weaponry, each requiring specialized training and expertise. The murmillo, equipped with a sword and shield, emphasized strength and defense, while the retiarius relied on speed and agility with a trident and net. The secutor, known as the "chaser," engaged in close combat with a helmet and sword, showcasing a blend of offense and defense in the arena.
Despite the fame and adulation they received from spectators, gladiators lived under the shadow of mortality, with the possibility of a fatal outcome in every match. Their performances in the arena were not only displays of skill and bravery but also tests of survival and endurance, where victory meant glory and defeat meant death. The life of a gladiator was a precarious balance between fame and danger, with the specter of death looming over every battle.

Gladiator Combat and Rules
Gladiator combat was a meticulously orchestrated dance of death, where skill, strategy, and sheer brutality intertwined in the sandy arena. The rules governing these deadly spectacles were strict, yet the stakes were always life and death. Each gladiator was a master of their chosen weapon, whether it be the murmillo with his sword and shield, the retiarius with his net and trident, or the secutor with his helmet and sword. These distinct classes of gladiators brought a variety of fighting styles and tactics to the arena, captivating the audience with their prowess and courage.
The combat itself was a choreographed display of violence, where every move and strike had a purpose. Gladiators were not mere brutes but skilled fighters who understood the art of combat. The crowd's roar fueled their adrenaline as they clashed in mortal combat, their fate hanging on the edge of a blade. Strategies were devised, weapons were wielded with precision, and tactics were employed to outwit opponents in the deadly dance of the arena.
Despite the brutality of gladiator combat, there were rules and regulations that governed the fights. Referees oversaw the matches, ensuring that fair play was maintained, and that neither combatant had an unfair advantage. Illegal moves were penalized, and injuries were tended to by medics on standby. The dramatic tension of the fights kept the audience on the edge of their seats, as they witnessed the clash of titans in the arena.
The gladiatorial games were not just about bloodshed, but also about honor, glory, and spectacle. The combatants were revered as heroes by some and condemned as savages by others. The ritualistic nature of the fights added a layer of drama and excitement to the proceedings, making each match a testament to the human spirit in the face of adversity.

Decline of Gladiator Games
As the Roman Empire entered a period of transformation and societal change, the once-thriving tradition of gladiator games began to wane. Several factors contributed to the decline of these brutal spectacles that had long captivated the hearts of Roman citizens.
One significant aspect that played a role in the decline of gladiator games was the shifting moral attitudes within Roman society. As Christianity began to spread and gain influence, the public perception of the violent and often deadly contests in the arena started to change. The increasing emphasis on compassion, mercy, and the value of human life clashed with the bloodshed and brutality of the gladiator games, leading to a gradual disapproval of such forms of entertainment.
Furthermore, economic pressures also played a part in the eventual demise of gladiator games. The cost of maintaining gladiatorial schools, providing armor and weapons, and organizing elaborate spectacles became increasingly burdensome for the Roman authorities. As financial strains mounted and priorities shifted, the lavish expenditures required to sustain the gladiator games became harder to justify, contributing to their decline.
Moreover, the tastes of the Roman populace began to evolve, seeking different forms of entertainment and diversion. With the emergence of new cultural trends and interests, the appeal of gladiator games started to diminish. The public's appetite for more sophisticated performances, theatrical productions, and chariot races grew, diverting attention away from the once-dominant gladiatorial contests.
In addition to these factors, the changing political landscape of the Roman Empire also played a role in the decline of gladiator games. As power dynamics shifted, emperors and rulers began to prioritize different forms of public spectacle and propaganda to maintain control and influence over the populace. The emphasis on other types of entertainment and political displays gradually marginalized the role of gladiator games in shaping public opinion and social cohesion.
Ultimately, a combination of moral, economic, cultural, and political factors led to the gradual decline and eventual disappearance of the ancient Roman gladiator games, marking the end of an era that had left a lasting impact on the history and culture of the Roman Empire.
1. Were gladiator games always deadly for the participants?
2. How were gladiators recruited and trained for combat?
3. What role did gladiator games play in Roman society and politics?
4. Were there any female gladiators in ancient Rome?
5. How did the portrayal of gladiators in popular culture differ from historical reality?

Legacy of Gladiator Games
Reflecting on the enduring legacy of gladiator games, it's fascinating to see how these ancient spectacles continue to captivate modern audiences. The influence of gladiator games extends beyond the confines of the Roman Colosseum, permeating popular culture, art, and literature with its tales of bravery and combat. Artists throughout history have been inspired by the dramatic imagery of gladiators in battle, immortalizing their stories on canvas and in sculpture. The gladiatorial ethos of courage, skill, and sacrifice has become a symbol of resilience and determination, resonating with individuals seeking to overcome adversity in their own lives.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What were the origins of gladiator games in ancient Rome?
The gladiator games in ancient Rome originated as funeral rites to honor deceased individuals. Over time, these spectacles evolved into grand events that captivated the Roman population, becoming a significant part of the culture and societal norms.
- What were the different types of gladiators and their characteristics?
There were various classes of gladiators in ancient Rome, each with distinct weapons, armor, and fighting styles. Some popular types included the murmillo, retiarius, and secutor, showcasing a wide range of combat techniques and skills.
- How did the decline of gladiator games come about in Roman society?
The decline of gladiator games in Roman society was influenced by several factors, including changing moral attitudes, economic pressures, and evolving entertainment preferences. These shifts eventually led to the discontinuation of this brutal form of entertainment.