The Art and Science of Restoring Historical Buildings
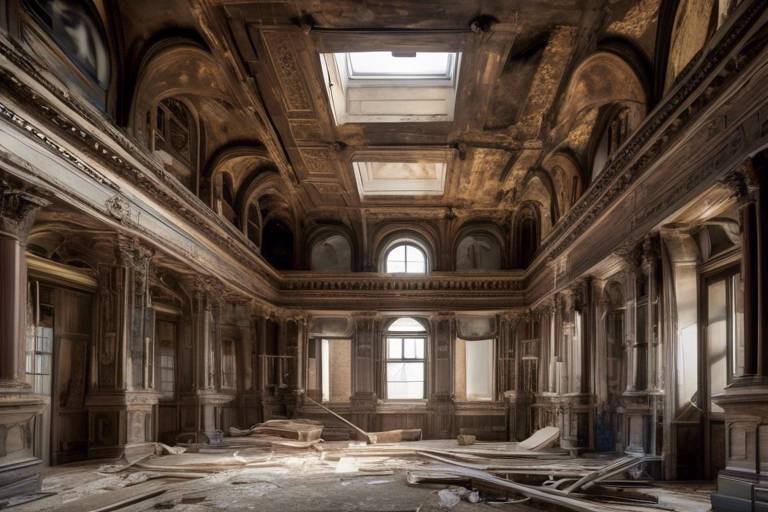
Restoring historical buildings is a delicate dance between art and science, where the past meets the present in a harmonious blend of preservation and innovation. It involves a meticulous process of uncovering the history embedded in the walls, roofs, and foundations of these architectural marvels, while also ensuring their structural integrity for future generations to admire and cherish.
Preservation challenges in restoring historical buildings are multifaceted, ranging from structural deterioration due to age and neglect to the evolving building codes that require updates to meet modern safety standards. Balancing the historical authenticity of these structures with the functional needs of contemporary society poses a unique set of challenges for restoration projects.
Historical research plays a crucial role in the restoration process, requiring a deep dive into original blueprints, archival materials, and construction techniques used during the building's inception. This meticulous study ensures that every detail of the restoration is historically accurate, preserving the essence of the past in the present.
Architectural conservation is the cornerstone of restoring historical buildings, focusing on maintaining the integrity of the original design while implementing necessary repairs and upgrades to ensure longevity. It is a delicate art of preserving the soul of the building while enhancing its structural stability for future generations to appreciate.
Community engagement is a vital component of restoration projects, as it fosters public support, raises awareness about the importance of architectural heritage, and involves local stakeholders in the preservation process. Engaging the community ensures that historical buildings remain a source of pride and identity for the neighborhoods they inhabit.
Incorporating sustainable practices in restoration projects is essential to minimize the environmental impact, reduce energy consumption, and ensure the long-term sustainability of historical buildings. By embracing eco-friendly solutions, restoration projects can preserve the past while safeguarding the future of these architectural treasures.
Technology has revolutionized the restoration and preservation of historical buildings, with advancements such as 3D scanning, Building Information Modeling (BIM), and virtual reality offering innovative solutions to complex restoration challenges. These technological tools enable architects and conservationists to visualize, analyze, and execute restoration projects with unprecedented precision and efficiency.
Financial considerations are a critical aspect of successful restoration projects, requiring careful planning, budgeting, and sourcing of funds to ensure the completion of the restoration process. Cost-effective restoration techniques coupled with strategic financial management are essential to preserving historical buildings within allocated budgets.
Educational initiatives play a pivotal role in spreading awareness about the significance of preserving historical buildings and promoting best practices in restoration. Workshops, seminars, and training programs serve as platforms for knowledge sharing, skill development, and advocacy for the preservation of architectural heritage.

Preservation Challenges
Preserving historical buildings comes with a myriad of challenges that require careful consideration and expertise. One of the primary preservation challenges is the structural deterioration that occurs over time due to natural elements and aging. This deterioration often necessitates extensive repairs and restoration work to ensure the building's stability and longevity. Additionally, changing building codes and regulations pose another hurdle in the preservation process. Balancing the need to comply with modern building standards while preserving the historical authenticity of the structure can be a delicate task that requires a deep understanding of both past architectural practices and current construction requirements.
When embarking on a restoration project, one of the key challenges is striking a harmonious balance between historical authenticity and modern functionality. While it is essential to maintain the original character and design of the building, incorporating modern amenities and technologies without compromising its historical integrity is a complex undertaking. Preservationists must carefully evaluate which elements can be updated or improved to enhance the building's usability while respecting its historical significance.
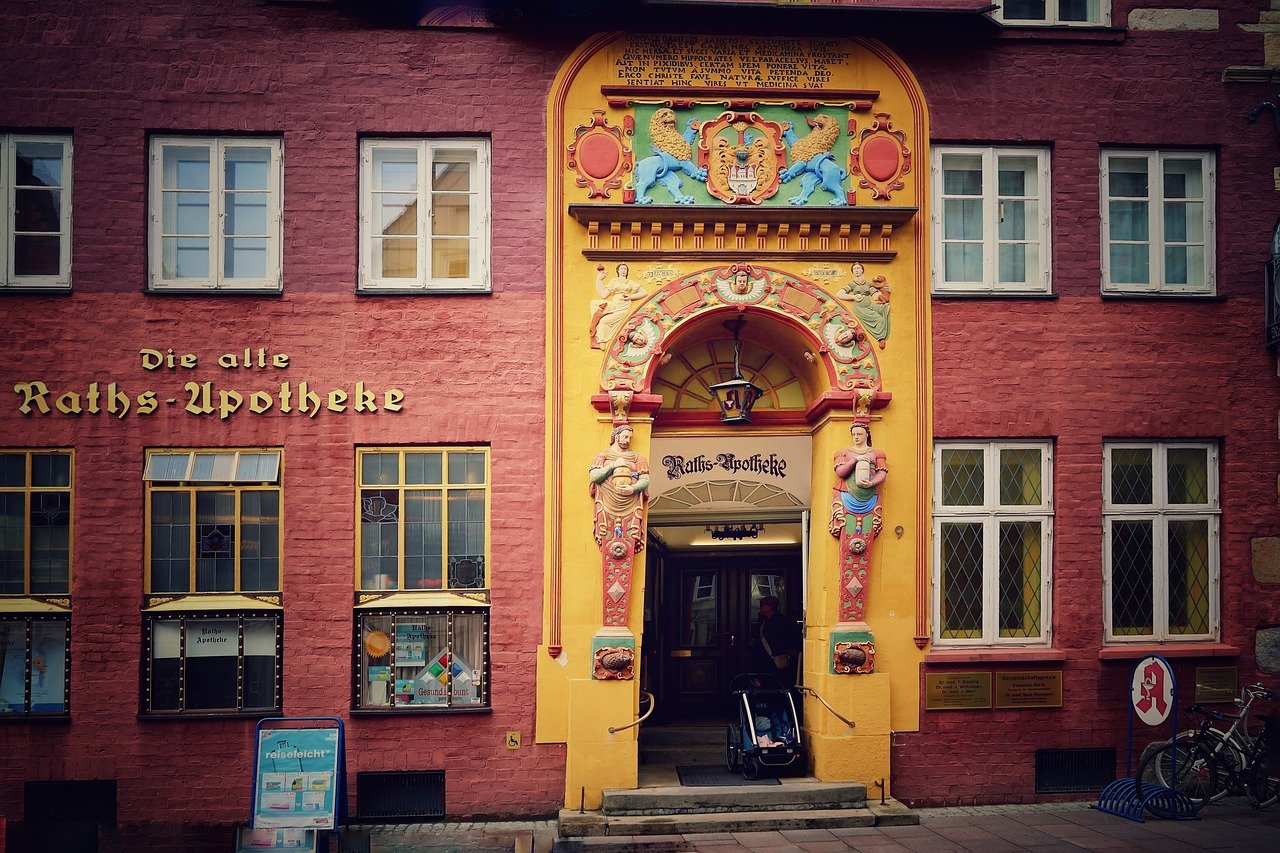

Historical Research
When it comes to restoring historical buildings, delving into the past is a crucial step in the process. Historical research forms the foundation upon which accurate restoration and preservation efforts are built. By studying original blueprints, materials, and construction techniques, preservation experts can ensure that the historical integrity of the building is maintained.
Imagine being a detective, but instead of solving crimes, you are uncovering the secrets of the past hidden within the walls of a centuries-old structure. Every detail matters, from the type of bricks used to the intricate designs etched into the cornices. It's like piecing together a puzzle where each fragment holds a piece of history waiting to be revealed.
Through historical research, experts gain insights into the architectural styles and craftsmanship of a bygone era. They unravel the stories embedded in the walls, deciphering the language of the past to bring the building back to life. It's a journey back in time, where every discovery adds a new layer to the narrative of the structure.
Moreover, historical research serves as a compass guiding restoration teams towards authenticity. By understanding the original vision of the architects and builders, preservationists can ensure that every restoration decision aligns with the spirit of the past. It's a delicate dance between honoring tradition and embracing innovation, where the past and present converge to create a harmonious blend of old and new.
Picture a historian meticulously combing through archives, a conservationist examining faded sketches, and an architect poring over faded blueprints. Each piece of information unearthed contributes to the tapestry of knowledge that informs the restoration process. It's a labor of love, a dedication to preserving the legacy of our architectural heritage for generations to come.
In conclusion, historical research is not just about uncovering facts; it's about breathing life into the past and ensuring that the echoes of history resonate through the halls of time. It's a tribute to those who came before us, a testament to the enduring beauty of our architectural legacy.
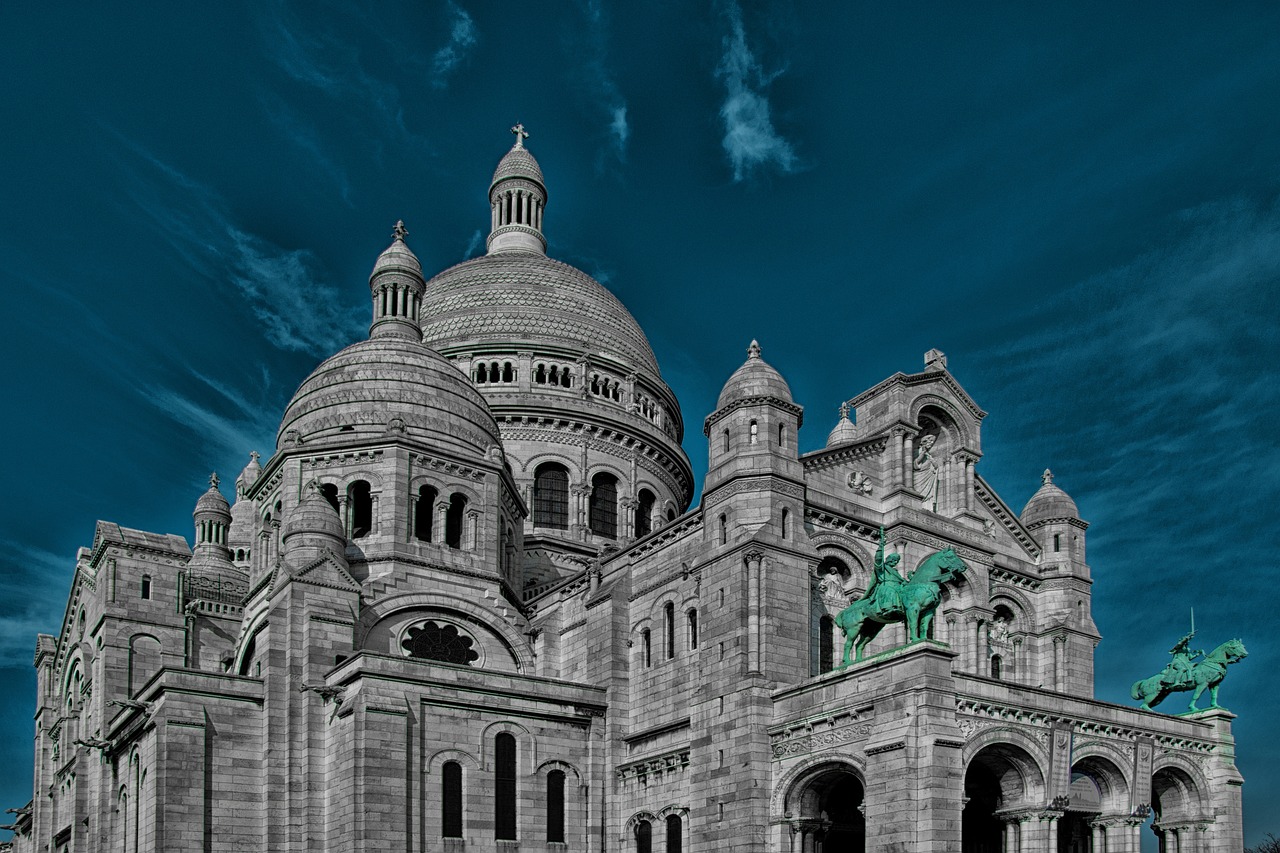

Architectural Conservation
Architectural conservation is a meticulous process that focuses on preserving the historical integrity of buildings while ensuring their structural stability and longevity. It involves a delicate balance between maintaining the original design and features of a historical structure and implementing necessary repairs and upgrades to meet modern standards.
One of the key aspects of architectural conservation is the use of authentic materials and traditional construction techniques to replicate the original building elements. This often requires extensive research into historical records, original blueprints, and archival photographs to accurately restore the building to its former glory.
In addition to preserving the physical aspects of historical buildings, architectural conservation also encompasses the conservation of intangible heritage, such as cultural significance and historical narratives associated with the structure. By understanding the historical context and cultural value of a building, conservationists can ensure that its heritage is safeguarded for future generations.
Collaboration with skilled craftsmen, architects, engineers, and conservation experts is essential in architectural conservation projects. By bringing together diverse expertise and knowledge, restoration teams can address complex challenges and develop innovative solutions to preserve historical buildings effectively.
Furthermore, architectural conservation extends beyond the physical restoration of buildings to include ongoing maintenance and monitoring to prevent deterioration and ensure the sustainability of the structure. Regular inspections, maintenance programs, and conservation plans are integral components of architectural conservation efforts.
Ultimately, architectural conservation is not just about preserving historical buildings as static monuments but also about revitalizing them as living spaces that contribute to the cultural and social fabric of communities. By respecting the past while embracing the present, architectural conservation ensures that historical buildings continue to inspire and enrich future generations.

Community Engagement
Community engagement is a crucial aspect of restoring historical buildings, as it involves fostering a sense of ownership and pride among local residents. By involving the community in restoration projects, it not only raises awareness about the historical significance of the building but also creates a sense of shared responsibility for its preservation.
One effective way to engage the community is through educational programs and workshops that provide insights into the history and architectural value of the building. These initiatives can help residents understand the importance of preserving historical structures and encourage active participation in restoration efforts.
Furthermore, community engagement can also involve seeking feedback and input from local stakeholders on proposed restoration plans. By incorporating the perspectives and preferences of the community, restoration projects can better reflect the values and identity of the neighborhood, fostering a stronger sense of connection and pride.
Organizing guided tours, open houses, and public events at the historical site can also be instrumental in engaging the community. These activities not only showcase the progress of the restoration work but also offer an opportunity for residents to interact with the building's history firsthand, creating a deeper appreciation for its cultural significance.
Moreover, establishing partnerships with local schools, universities, and cultural organizations can further enhance community engagement efforts. By involving educational institutions in the restoration process, it not only provides valuable learning opportunities for students but also instills a sense of stewardship for historical preservation in future generations.
In summary, community engagement is not just about involving people in restoration projects; it is about building a sense of community pride, ownership, and responsibility towards preserving historical buildings for future generations to appreciate and enjoy.

Sustainable Practices
When it comes to restoring historical buildings, incorporating sustainable practices is crucial for ensuring the long-term preservation of these architectural treasures. Sustainable practices not only help minimize the environmental impact of restoration projects but also contribute to the overall sustainability of historical structures. By implementing eco-friendly techniques and materials, preservation efforts can be more effective and environmentally conscious.
One sustainable practice commonly used in restoration projects is the integration of energy-efficient systems. This involves upgrading the building's heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems to reduce energy consumption and lower carbon emissions. By utilizing modern, energy-saving technologies, historical buildings can become more environmentally friendly while maintaining their historical charm.
Additionally, the use of sustainable building materials plays a significant role in preserving historical structures. Opting for materials that are durable, recyclable, and environmentally friendly helps reduce the overall environmental impact of restoration work. From reclaimed wood to energy-efficient windows, choosing sustainable materials not only benefits the environment but also enhances the longevity of the building.
Furthermore, implementing water conservation measures is another important aspect of sustainable practices in historical building restoration. By installing water-saving fixtures, implementing rainwater harvesting systems, and promoting water-efficient landscaping, restoration projects can reduce water waste and contribute to overall sustainability. Conserving water resources is essential for the preservation of historical buildings and the surrounding environment.
Moreover, incorporating green spaces and sustainable landscaping techniques around historical buildings can enhance their overall sustainability. Green roofs, native plantings, and permeable paving are examples of sustainable landscaping practices that can improve energy efficiency, reduce stormwater runoff, and create a healthier environment for the building and its occupants. By integrating green elements into the restoration process, historical buildings can become more resilient and environmentally friendly.

Technology in Restoration
Technology plays a pivotal role in the restoration and preservation of historical buildings, bringing innovative solutions to age-old challenges. One of the groundbreaking advancements in this field is 3D scanning, which allows for detailed digital documentation of structures, aiding in accurate restoration planning and analysis. By capturing precise measurements and intricate details, 3D scanning enables restoration experts to create virtual models of historical buildings with unparalleled accuracy.
Another cutting-edge technology transforming the restoration landscape is Building Information Modeling (BIM). BIM facilitates the creation of comprehensive digital representations of historical structures, incorporating information about materials, structural elements, and building systems. This digital tool enhances collaboration among architects, engineers, and preservationists, streamlining the restoration process and ensuring a holistic approach to conservation.
Virtual reality (VR) is revolutionizing the way stakeholders interact with historical buildings during the restoration process. By immersing users in realistic virtual environments, VR technology enables architects and conservationists to visualize proposed changes, test different design scenarios, and assess the impact of interventions before implementation. This immersive experience enhances decision-making, fosters creativity, and ensures that restoration projects align with preservation goals.

Financial Considerations
Historical building restoration is a delicate dance between preserving the past and adapting to the present. It involves a unique blend of artistry and scientific precision to breathe new life into structures that have weathered the test of time. From ancient cathedrals to historic homes, each building holds a story waiting to be told through careful restoration.
When embarking on a historical building restoration project, financial considerations are paramount. The costs involved in restoring and maintaining these architectural gems can be substantial, requiring careful planning and budgeting to ensure the project's success. Funding sources play a crucial role in determining the scope and scale of the restoration efforts, whether through government grants, private donations, or corporate sponsorships.
Moreover, implementing cost-effective restoration techniques is essential to maximize the impact of the allocated budget. Balancing the need for quality craftsmanship with budget constraints is a common challenge faced by restoration teams. By carefully evaluating the most cost-efficient methods for repairs and upgrades, project managers can stretch their funding further without compromising on the integrity of the historical structure.
Additionally, ongoing maintenance costs should be factored into the financial considerations of historical building restoration. Ensuring the long-term sustainability of the restored structure requires a proactive approach to maintenance, including regular inspections, repairs, and preservation efforts. By planning for future maintenance needs during the restoration process, stakeholders can safeguard the building's longevity and minimize unexpected expenses down the road.
1. How long does a typical historical building restoration project take?
2. What are the common challenges faced during the restoration process?
3. How can community engagement contribute to the success of a restoration project?
4. Are there any specific regulations or guidelines for preserving historical buildings?
5. What role does technology play in modern restoration efforts?

Educational Initiatives
Educational initiatives are crucial in raising awareness about the significance of preserving historical buildings and promoting best practices in restoration. Workshops, seminars, and training programs serve as platforms for sharing knowledge and expertise among professionals, enthusiasts, and the general public. These initiatives not only educate individuals about the historical and cultural value of heritage structures but also provide insights into the technical aspects of restoration and conservation.
Through educational programs, participants gain a deeper understanding of the challenges involved in preserving historical buildings, such as the impact of environmental factors, the importance of using authentic materials, and the significance of traditional construction techniques. Hands-on workshops and practical demonstrations allow attendees to experience firsthand the intricacies of restoration work, fostering a greater appreciation for the craftsmanship and artistry of past architectural styles.
Furthermore, educational initiatives facilitate networking opportunities and collaboration among experts in the field, encouraging the exchange of ideas and innovative approaches to heritage conservation. By engaging with a diverse range of professionals, students, and community members, these programs contribute to a collective effort to safeguard our architectural heritage for future generations.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What are the common challenges faced in restoring historical buildings?
Preserving historical buildings comes with various challenges such as structural deterioration, evolving building codes, and the delicate balance between maintaining historical authenticity and incorporating modern functionality.
- How important is historical research in the restoration process?
Historical research is crucial in restoration projects as it involves studying original blueprints, materials, and construction techniques to ensure accurate preservation of historical buildings, maintaining their architectural significance.
- What role does community engagement play in restoration projects?
Community engagement is vital as it helps garner public support, raise awareness, and involve local stakeholders in the preservation process, fostering a sense of ownership and pride in the historical heritage of the buildings.
- How do sustainable practices contribute to the restoration of historical buildings?
Incorporating sustainable practices in restoration projects helps minimize environmental impact, reduce energy consumption, and ensure the long-term sustainability of historical buildings, preserving them for future generations.
- What technological advancements are revolutionizing the restoration of historical buildings?
Technological advancements such as 3D scanning, Building Information Modeling (BIM), and virtual reality are transforming the way historical buildings are restored and preserved, enhancing accuracy and efficiency in the restoration process.